Hovedbudskap
Hypertensjon hos diabetikere skal behandles intenst
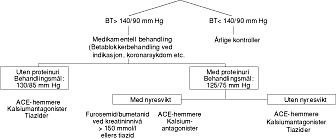
Anbefalte midler er tiazider, kalsiumantagonister og ACE-hemmere, eventuelt i kombinasjon
Betablokkere er sannsynligvis lett diabetogene, men kan benyttes dersom man ønsker å redusere samlet kardiovaskulær risiko
Behandlingsmål skal relateres til tilstedeværelsen av proteinuri
- 1.
Gress TW, Nieto FJ, Shahar E, Wofford MR, Brancati FL for the Atherosclerosis Risk in Community Study. Hypertension and antihypertensive therapy as risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 2000; 342: 905.
- 2.
Hansson L, Lindholm LH, Niskanen L, Lanke J, Hedner T, Niklason A et al. Effect of angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibition compared with conventional therapy on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in hypertension: the Captopril Prevention Project (CAPPP) randomised trial. Lancet 1999; 352: 611 – 6.
- 3.
UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. Tight blood pressure control and risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes: UKPDS 38. BMJ 1998; 317: 703 – 13.
- 4.
Fagard RH, Staessen JA. Treatment of isolated systolic hypertension in the elderly: the Syst-Eur trial. Systolic Hypertension in Europe (Syst-Eur) Trial Investigators. Clin Exp Hypertens 1999; 21: 491 – 7.
- 5.
Estacio RO, Jeffers BW, Gifford N, Schrier RW. Effect of blood pressure control on diabetic microvascular complications in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2000; 23 (suppl 2): B54-B64.
- 6.
Tatti P, Pahor M, Byington RP, Di Mauro P, Guarisco R, Strollo G et al. Outcome results of the Fosinopril Versus Amlodipine Cardiovascular Events Randomized Trial (FACET) in patients with hypertension and NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1998; 21: 597 – 603.
- 7.
Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation (HOPE) Study Investigators. Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Lancet 2000; 355: 253 – 9.
- 8.
The ALLHAT officers and coordinators for the ALLHAT collaborative research group. Major cardiovascular events in hypertensive patients randomized to doxazosin vs chlortalidone: the Antihypertensive and Lipid-Lowering Treatment to Prevent Heart Attack Trial (ALLHAT). JAMA 2000; 283: 1967 – 75.
- 9.
Chaturvedi N, Sjolie AK, Stephenson JM, Abrahamian H, Keipes M, Castellarin A et al. Effect of lisinopril on progression of retinopathy in normotensive people with type 1 diabetes. Lancet 1998; 351: 28 – 31.
- 10.
British Cardiac Society, British Hyperlipidemia Association, British Hypertension Society, British Diabetic Association. Joint British recommendations on prevention of coronary heart disease in clinical practice: summary. BMJ 2000; 320: 705 – 8.
- 11.
Curb JD, Pressel SL, Cutler JA, Savage PJ, Applegate WB, Black H et al. Effect of diuretic-based antihypertensive treatment on cardiovascular disease risk in older diabetic patients with isolated systolic hypertension: Systolic Hypertension in the Elderly Program Cooperative Research Group. JAMA 1996; 276: 1886 – 92.
- 12.
Brown M, Palmer CR. Castaigne A, Leeuw PW, Mancia G, Rosental T et al. Morbidity and mortality in patients randomised to double blind treatment with a long-acting calcium-channel blocker or diuretic in the International Nifedipine GITS study: Intervention as a goal in Hypertension Treatment (INSIGHT). Lancet 2000; 356: 366 – 72.
- 13.
Hanson L, Hedner T, Lund-Johansen P, Kjeldsen S, Lindholm LH, Syvertsen JO et al. Effects of calsiumantagonists compared with diuretics and betablockers on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in hypertension: the Nordic Diltiazem (NORDIL) Study. Lancet 2000; 356: 359 – 65.